It is an important disease problem in nurseries, vegetative multiplication areas, seed and clonal orchards of many forestry species viz., Acacia, Albizia, Bamboos, Casuarina, Dalbergia, Eucalyptus, Gmelina, Melia, Neem, Cadamba, Sandal, Teak, etc.
Many forestry species such as Acacia, Albizia, Bamboos, Casuarina, Dalbergia, Eucalyptus, Gmelina, Melia, Neem, Cadamba, Pterocarpus, Sandal, Swietenia, Teak, etc
Soil and root borne pathogens like Fusarium, Rhizoctonia, Sclerotium etc. and bacteria viz., Pseudomonas solanacearum are the causal organisms reported on many important forestry crops.
1. Paling of foliage and leaf shedding and subsequent death of the seedlings.
2. Premature defoliation.
The disease can be managed by an integrated approach involving measures such as sanitation, cultural practices and use of fungicides. Avoid high water stagnation in nurseries and young plantations. Proper water drainage facility should be provided in the low lying areas in nurseries and young plantations. Potting mixtures should be properly sterilized (dried under the sun light) before putting in nursery beds and filling in containers. Application of suitable fungicide by soil drenching with 0.2% Bavistin or Dithane M-45 at monthly intervals effectively controls the disease. After 15 to 30 days of fungicidal application, the seedlings need to be applied with bio-control agents such as Pseuodomonas fluorescence and Trichoderma viride for effective management of the disease.
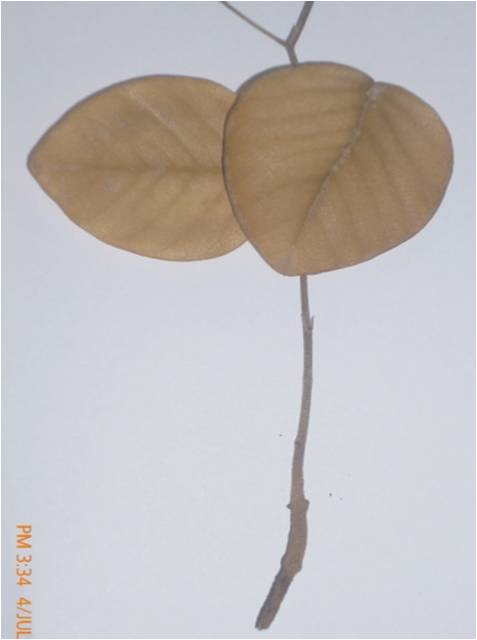
Root rot disease symptoms of Thesoesia populnea (Poovarasu)

Root - rot disease symptoms of Melia dubia caused by Fusarium solani

Root - rot disease symptoms of Pterocarpus santalinus caused by Fusarium sp.