It is one of the important diseases in nurseries, vegetative multiplication areas, seed and clonal orchards of many forestry tree species viz., Acacia, Albizia, Bamboos, Casuarina, Dalbergia, Eucalyptus, Gmelina, Melia, Neem, Cadamba, Pterocarpus, Sandal, Swietenia, Teak, Terminalia, etc.
Many forestry species such as Acacia, Albizia, Bamboos, Casuarina, Dalbergia, Eucalyptus, Gmelina, Melia, Neem, Cadamba, Pterocarpus, Sandal, Swietenia, Teak, Terminalia, etc are affected by this disease.
Different fungi like Alternaria, Cercospora, Colletotrichum, Curvularia, Cylindrocladium, Fusarium, Macrophomina, Phoma, Phomopsis, Pestalotiopsis, Phyllachora, Phyllosticta Pseudocercospora, etc. and bacteria viz., Xanthomonas and Pseudomonas are the causal organisms reported on many forestry crops.
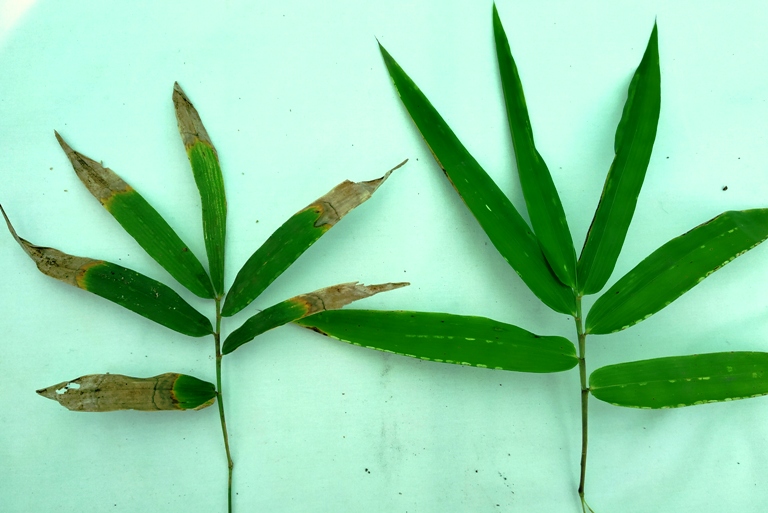
1. Water soaked lesions on the tip of the leaves. Later, it spreads to leaf margin and finally the whole leaf loses its green colour.
2. The infected plants show water soaked grayish brown patches that enlarge rapidly and cover a large part or the entire lamina.
3. The infected leaves present a high blighted appearance and severely infected seedlings show premature defoliation.
4. The disease spreads rapidly after initial appearance in patches, causing large scale mortality of nursery stock.
5. Infected plants exhibit blighting of shoots and leaves and subsequent colonization by pathogens fasten blighting.
6. The blighted leaves often show holes in the infected portion as a result of shedding of infected tissues during heavy rains.
7. The infected leaves dry up and are eventually shed.
8. The disease spreads laterally in the nursery through overlapping foliage of the adjoining seedlings often resulting in group blighting of seedlings.
9. In each case of severe infection, defoliation is high.
The diseases can be managed by:
a) Cultural practices aimed at favoring plant growth and discouraging the growth of plant pathogen.
b) Severely infected plants need to be kept in isolation in order to prevent the spread of the disease to other healthy plants.
c) Use of any one of fungicides like Bavistin, Blitox, Captof, Dithane M-45, Mancozeb at fortnightly intervals.
Leaf blight disease on Gmelina arborea
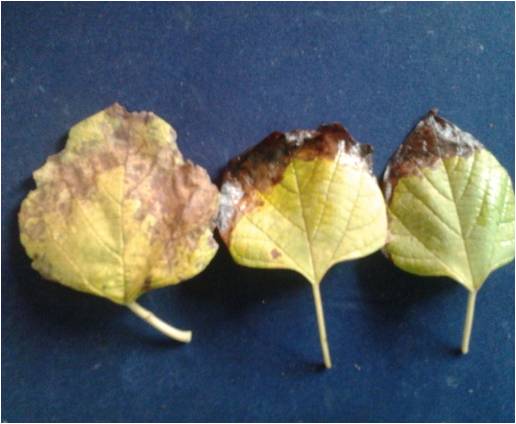

Leaf blight disease on Pongamia pinnata
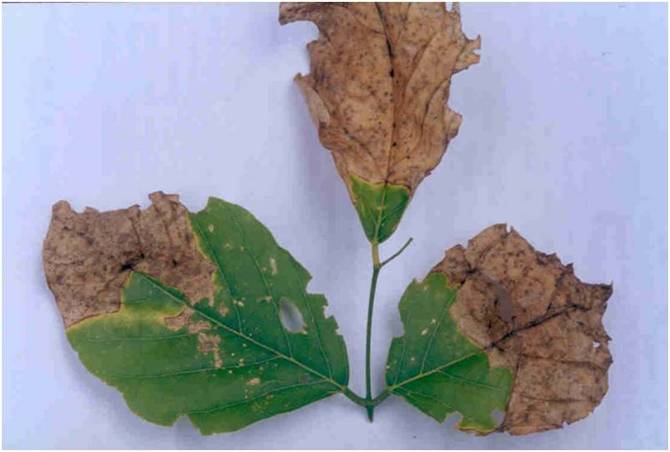

Leaf blight disease symptoms of Bauhina sp.

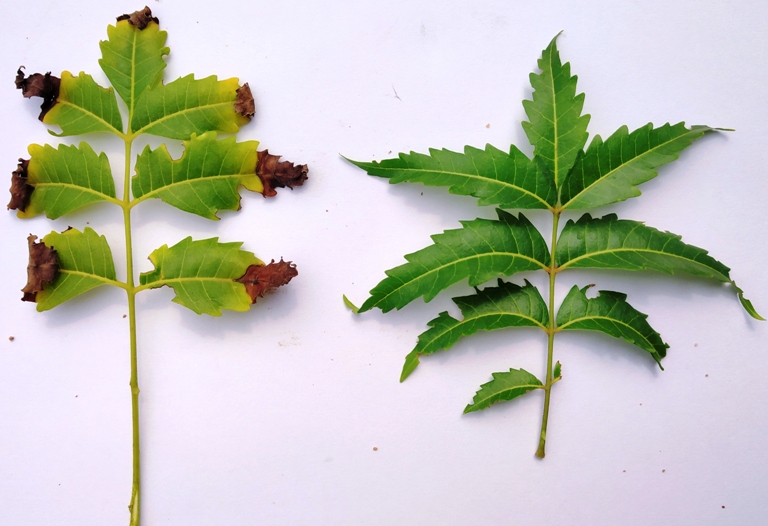
Leaf blight disease symptoms of Neem and healthy twig

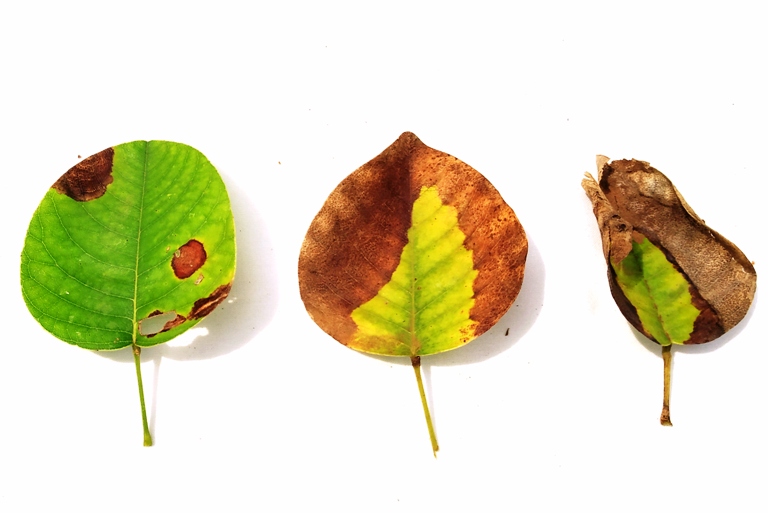
Leaf blight disease symptoms of Swietenia mahagony

Leaf blight disease symptoms of Pterocarpus santalinus (Red Sanders)

Leaf blight disease symptoms of Pterocarpus santalinus

Leaf blight disease symptoms of Bamboo