It is an important disease in nurseries, vegetative multiplication areas, seed and clonal orchards of different tree species viz., Acacia, Albizia, Bamboos, Casuarina, Dalbergia, Eucalyptus, Gmelina, Melia, Neem, Cadamba, Pterocarpus, Sandal, Swietenia, Teak,Terminalia, etc. It has been recorded as a serious problem in clonal nursery, VMGs and seed and clonal orchards of different tree species.
Many forestry species such as Acacia, Albizia, Bamboos, Casuarina, Dalbergia, Eucalyptus, Gmelina, Melia, Neem, Cadamba, Pterocarpus, Sandal, Swietenia, Teak, Terminalia, etc
Different fungi like Alternaria, Cercospora, Colletotrichum, Curvularia, Cylindrocladium, Fusarium, Macrophomina, Phoma, Phomopsis, Pestalotiopsis, Phyllachora, Phyllosticta Pseudocercospora, etc. and bacteria viz., Xanthomonas and Pseudomonas are the causal organisms reported on many forestry crops.
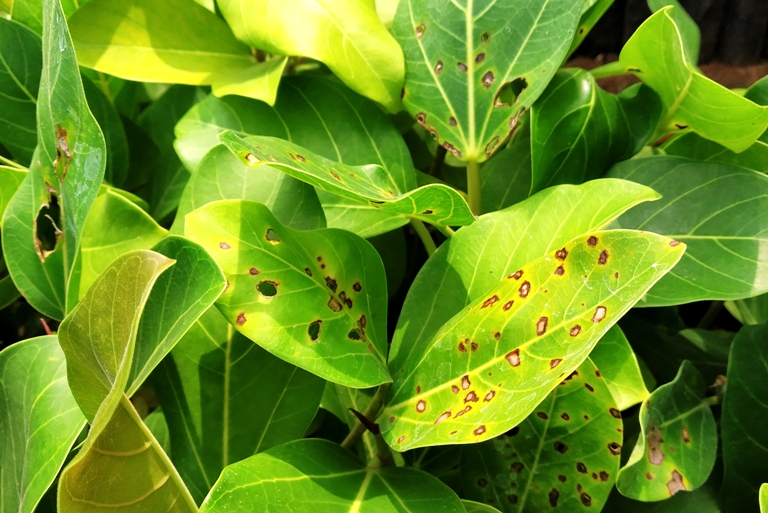
1. Infected leaves exhibit different coloured spots which are circular and irregular in shape. Depending up on the pathogen, the colour of the spot varies.
2. Infection spots are grey, brown, black, yellow, white and dark brown, vary in size and shape and coalesce to form larger spots.
3. The spots are round to irregular, greyish-brown which sometimes cover the entire leaf surface.
4. The pathogen sporulates on the lower surface of the leaves of some of the host plants.
5. The heavily infected leaves are shed prematurely.
6. The necrotic tissues usually fall off resulting in formation of shot holes symptoms.
7. The infected leaves present a blighted appearance and are eventually shed.
8. Severely infected seedlings show premature defoliation.
The disease can be managed by
a) Cultural practices aimed at favoring plant growth and discouraging the growth of plant pathogen
b) Severely infected plants need to be kept in isolation in order to prevent the spread of the disease to other healthy plants
c) Use of any one of fungicides like Blitox, Captof, Dithane M-45, Mancozeb at fortnightly intervals.
Leaf spot disease symptoms on Albizia lebbeck

Leaf spot disease symptoms on Dalbergia latifolia
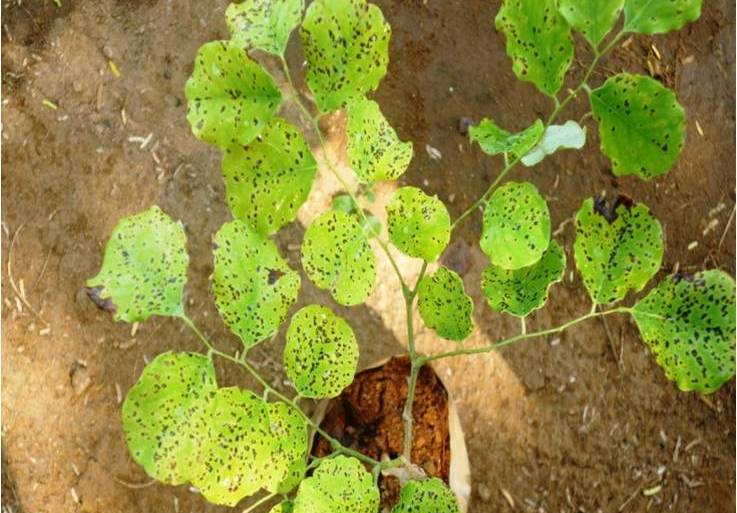

Leaf spot disease symptoms of Eucalyptus
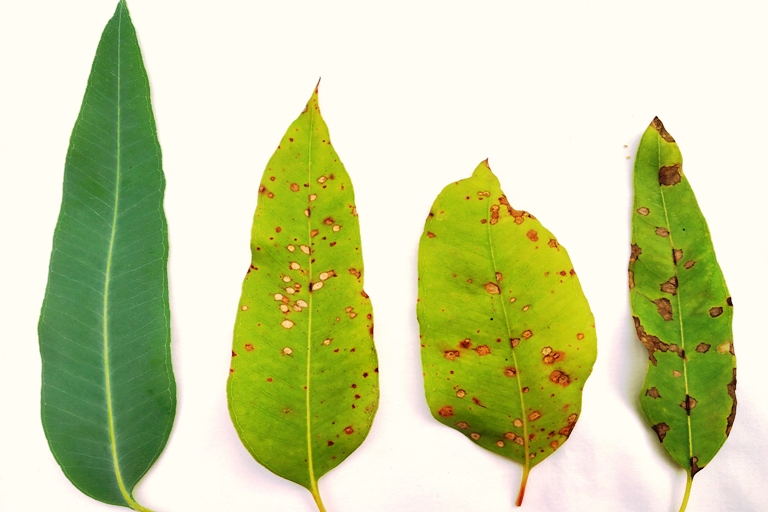

Leaf spot disease symptoms of Bamboo
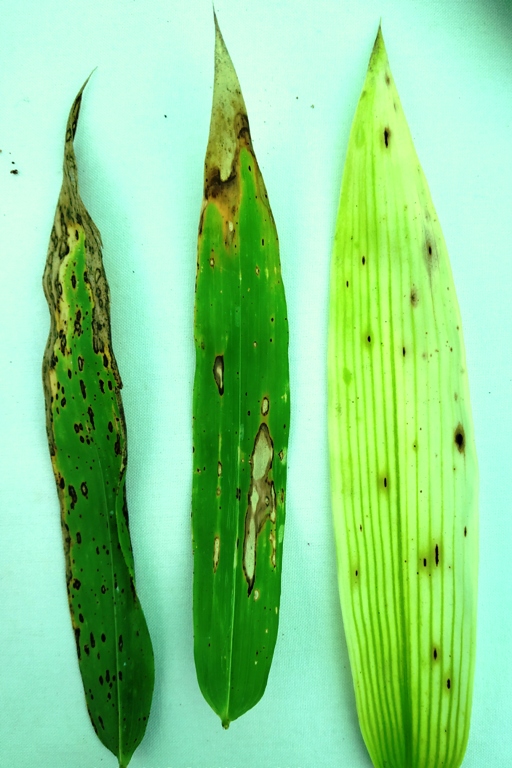

Leaf spot disease symptoms of Terminalia catappa

Leaf spot disease symptoms of Ficus benghalensis
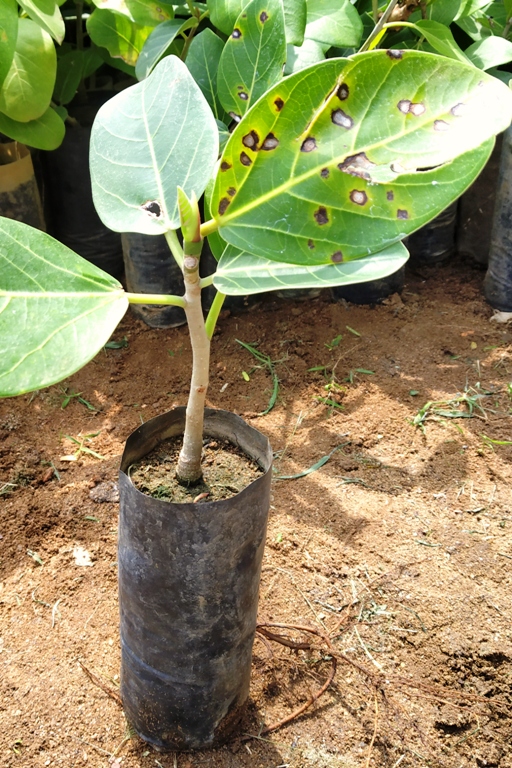

Leaf spot disease symptoms of Ficus benghalensis